Introduction
The A1c test, sometimes known as the glycated hemoglobin test, is a simple blood test done in healthcare settings to check how well your body is managing blood sugar over a period of about three months. Understanding A1c Test Results is crucial for people with diabetes or at risk of developing it because it provides insight into average blood sugar levels without having to undergo constant monitoring.
When you hear about A1c, it’s all about hemoglobin—specifically, the percentage of hemoglobin that’s coated with sugar, or glucose. This happens because glucose in the bloodstream naturally attaches to the hemoglobin in red blood cells. By measuring this percentage, doctors can get an idea of how high or low your blood sugar has been, on average, over the previous few months.
So, who should be taking this test? It’s generally recommended for anyone who has been diagnosed with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, and also for those who might be predisposed to developing diabetes because of factors like family history or obesity. It’s a pretty reliable test as it gives doctors a bigger picture of your glucose level over time rather than a one-off measurement.
For people who have diabetes, regular monitoring through the A1c test helps in assessing how well the current management plan is working. It’s also useful in identifying trends or patterns that might suggest a need to tweak diet, exercise, or medication strategies. It’s always important to talk with your healthcare provider to know how often you should have your A1c checked based on your unique health needs.
Table of Contents
The Importance of A1c Tests in Diabetes Management
A1c tests are crucial for:
- Diagnosing Diabetes: It helps identify whether someone is diabetic or at risk (prediabetic).
- Monitoring Diabetes Management: Regular tests show if blood sugar levels are being effectively controlled.
- Adjusting Treatment Plans: Results guide healthcare providers in making changes to medication, diet, or exercise routines.
- Setting Personal Health Goals: Knowing your A1c levels helps you and your doctor set achievable targets for better diabetes management.
The A1c test serves as a critical diagnostic tool, not just for identifying diabetes but also for monitoring the progression of the condition. Whether you’re already managing diabetes or on the verge of prediabetes, your A1c results can guide important healthcare decisions and help in setting long-term goals.
One of the key roles of the A1c test is in monitoring how well diabetes is controlled. By giving a more comprehensive view of blood sugar levels over time, it helps both patients and healthcare providers decide if current treatment plans are effective. Are the medications working? Is the diet suitable? These questions can be addressed effectively through this test.
Treatment decisions often hinge on A1c results. If the levels are outside the desired range, it might indicate a need to adjust medications or change lifestyle practices. Healthcare providers often use these results to personalize treatment plans, ensuring they align with an individual’s specific health profile.
Setting personal health goals becomes more manageable with clear A1c targets in mind. Knowing where you stand in the test can motivate essential changes, whether that’s incorporating more exercise or refining your meal choices. It’s about understanding the impact of your day-to-day decisions on your overall diabetes management strategy.
Discussing A1c results with your healthcare provider can lead to a deeper understanding of how different factors affect your condition, helping you engage more actively in your health journey. It’s not just about numbers but how those numbers translate into actionable steps for a healthier life.
Decoding Your A1c Test Results
A1c test results can sometimes feel like just a string of numbers, but they tell an important story about your health. Typically, results are presented as percentages. These percentages represent the amount of hemoglobin that is sugar-coated, so to speak.
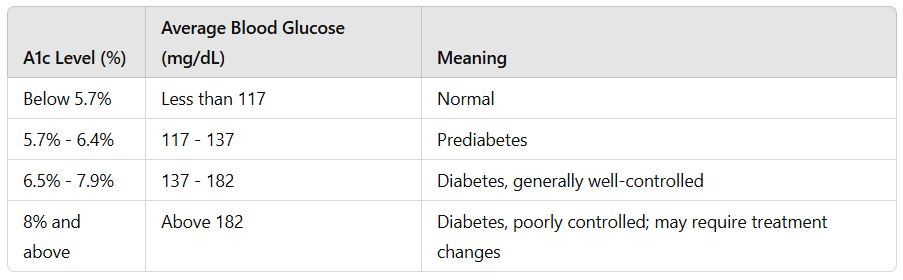
A1c levels under 5.7% are usually considered normal, indicating that your blood sugar levels are well-managed. If your A1c falls between 5.7% and 6.4%, this range is often regarded as prediabetes, suggesting you’re at an increased risk for developing diabetes. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher is a vital indicator used to diagnose diabetes.
Understanding these ranges is key, especially if you have diabetes. Regular testing can inform whether lifestyle or medication adjustments are necessary to achieve or maintain optimal control of blood sugar levels.
The frequency of A1c testing can differ from person to person. For those managing diabetes, it’s common to have the test done at least twice a year. However, if treatment has changed or results have been off target, more frequent testing—such as quarterly—might be recommended by your healthcare provider.
Having these numbers in your back pocket allows you and your healthcare team to map out a clear plan for your health. It’s about being proactive and using the data as a steppingstone to better manage your glucose levels. Keeping track of these figures empowers you to make informative and strategic decisions that support your overall well-being.

Factors Influencing A1c Results
Various elements can impact your A1c results, including:
- Diet: High carbohydrate intake can elevate your A1c.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps lower A1c levels by improving insulin sensitivity.
- Medications: Diabetes medications, as well as some other prescriptions, can affect blood sugar levels.
- Health Conditions: Conditions like anemia or kidney disease may skew results.
- Age and Ethnicity: Different ethnic groups and older adults may naturally exhibit higher A1c levels.
Your A1c results could be affected by a myriad of factors, many of which you might not initially consider. Diet and lifestyle are massive players. Eating patterns, particularly carbohydrate intake, can sway your results significantly. Maintaining a balanced diet with controlled portions helps manage these levels better.
Exercise, too, plays an integral role. Regular physical activity helps in maintaining steady glucose levels, directly impacting A1c results. Even small steps, like walking or choosing stairs over elevators, contribute positively to your numbers.
Different medications, whether for diabetes or other conditions, can also influence A1c levels. Having a discussion with your healthcare provider about how these medications interact can provide valuable insights.
Ethnicity and age add another layer of complexity, as some ethnic groups naturally tend to have higher A1c levels, and older individuals might see different ranges due to changes in red blood cell turnover. Understanding these variations helps in contextualizing your results.
Certain biological factors and medical conditions, such as anemia or chronic kidney disease, can skew your A1c, making it look higher or lower than it actually is. It’s important to assess these factors with a healthcare provider to get a clear picture of your actual blood sugar control.
Steps to Improve Your A1c Levels
- Adjust Your Diet: Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and controlled carbohydrates. Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks.
- Increase Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Incorporate strength training for better insulin sensitivity.
- Manage Stress Levels: Practice mindfulness, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress, which can raise blood sugar levels.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly: Use continuous glucose monitors or traditional methods to track your levels.
- Work Closely with Healthcare Providers: Regular consultations help in tweaking your treatment plan based on your A1c levels.
Lowering your A1c involves making some thoughtful lifestyle changes, which can significantly improve your overall health. Adjusting your diet is a great starting point. Focusing on whole foods and watching carbohydrate intake can make a big difference. Incorporating more vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while cutting back on processed foods often helps.
Exercise is another effective way to manage and lower A1c levels. Regular physical activity, whether it’s walking, cycling, or any form of exercise you enjoy, helps your body use insulin more efficiently. Finding something you love and making it a regular part of your routine can yield substantial benefits.
Working closely with healthcare professionals can ensure your approach aligns with your needs. They might suggest adjustments to your medication or introduce tools like continuous glucose monitors to keep better track of blood sugar fluctuation.
Remember, reducing stress plays an important role too. High stress levels can lead to hormone changes that might increase blood sugar. Techniques like meditation, yoga, or even hobbies that relax you can be beneficial.
Setting achievable goals and tracking your progress can motivate you to stick with these changes. Small, consistent steps can lead to substantial long-term improvements in your A1c.
Innovations and Advances in A1c Testing
Recent advances include:
- At-Home A1c Test Kits: Allow for easier and more frequent monitoring.
- Integration with Digital Health Apps: Devices that sync A1c data with other health metrics for a holistic view.
- Non-Invasive Methods: Ongoing research aims to develop tests that require minimal blood samples.
The field of A1c testing is continuously evolving, bringing new technologies and methods to the table. One of the exciting advancements is the development of at-home A1c test kits. These kits offer convenience and ease for individuals who require regular monitoring without frequent trips to the clinic.
Digital health technologies are also stepping up. Smart devices and apps are now capable of integrating A1c data with other health metrics, providing a more comprehensive view of an individual’s overall health. These technological solutions help in identifying patterns and making informed decisions quickly.
The continuous research into A1c testing aims at making the process more accurate and less invasive. Innovations in biomarker analysis and more sophisticated algorithms are helping achieve higher precision in results, which is essential for effective diabetes management.
One challenge remains the accessibility and affordability of these advanced testing methods. However, ongoing efforts are directed at making these technologies more available to broader populations, ensuring that everyone gets the benefit of precise and timely diabetes monitoring.
This wave of innovation not only adds convenience but also empowers individuals by providing more tools to manage their health proactively. Staying informed about these advances allows individuals to advocate for better, more personalized healthcare solutions.
Common Myths and Misunderstandings about A1c Tests
- Myth: “A1c is the only measure of diabetes management.”
Fact: Daily blood glucose monitoring is equally important. - Myth: “A high A1c means you’re failing at diabetes management.”
Fact: It’s a guide to adjust your plan and improve, not a judgment. - Myth: “The test only shows recent diet changes.”
Fact: It reflects average blood sugar levels over three months.
There are plenty of misconceptions surrounding A1c tests, which can often lead to confusion or mismanagement of diabetes. It’s crucial to clear these up to ensure everyone has the right information.
One common myth is that A1c is the only measure of managing diabetes. While it’s a reliable indicator of long-term blood sugar levels, it doesn’t replace daily glucose monitoring, especially for those managing insulin doses. Regular blood sugar tests are still essential.
Another misunderstanding is thinking A1c results are influenced solely by recent dietary choices. While a single meal won’t drastically shift your A1c, patterns of eating habits over time certainly will. It’s the long-term trends that matter most, not short-term fluctuations.
Some people believe that a good A1c result means diabetes management doesn’t need to change. Even if your A1c numbers are within a healthy range, it’s critical to continue regular consultations with your healthcare provider to keep things on track and make informed decisions.
Finally, there’s often confusion between A1c and other types of glucose tests. While fasting glucose and daily blood sugar tests give immediate snapshots, the A1c test provides a broader perspective over months—an essential piece of the puzzle, but not the sole source of information.
A Patient’s Perspective
Understanding the technicalities of A1c testing is crucial, but hearing from those who live with it every day adds an invaluable dimension to our understanding. Real stories from individuals managing their diabetes with A1c testing illuminate the challenges and successes that come with it.
For many, the first A1c test is a wake-up call. John, diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, describes his initial results as a catalyst for change. Faced with an elevated A1c, he realized the immediate need to overhaul his lifestyle, focusing on healthier eating and incorporating more exercise into his routine.
Another patient, Maria, shares her experience of fluctuations in her A1c results. Despite her diligent efforts, she found her levels occasionally higher than expected. This taught her the complexities of diabetes management and the impact of factors like stress and sleep on her blood sugar.
For Jane, keeping her A1c in check became a team effort. Involving her family in meal planning and physical activities turned her individual challenge into a shared journey. Her story highlights the importance of a support system in navigating the ups and downs of diabetes.
Each story reinforces the idea that while managing diabetes is anything but straightforward, the A1c test provides essential feedback to guide ongoing adjustments. It’s about understanding the numbers and using them as a tool to inform, motivate, and navigate this lifelong journey.
A1c Test Results
For those navigating the world of A1c and diabetes, resources and support networks play a significant role in successful management. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or have been managing your condition for years, seeking out these supports can make a big difference.
Healthcare providers remain a key resource, offering not just testing but guidance on interpreting results and adjusting treatment plans. Regular check-ins provide the opportunity to discuss concerns and refine strategies based on your A1c outcomes.
Community support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences, tips, and encouragement. Whether in-person or online, these groups can offer emotional support and practical advice from people who understand the daily realities of living with diabetes.
Educational resources, such as workshops or diabetes management courses, offer structured learning opportunities to stay informed about the latest developments in diabetes care. Many organizations provide these resources for free or at a low cost.
Nutrition and fitness professionals can also augment your health strategy, helping tailor plans that align with your A1c goals. Personalized advice from experts ensures your approach reflects the latest understanding of effective diabetes management.
Lastly, utilizing digital tools like apps and online forums can help you track progress, set reminders, and access a wealth of information at your fingertips. Staying connected with these resources keeps you well-informed and empowered to make the best choices for your health.
Wrapping Things Up
The A1c test stands as a cornerstone in the management and diagnosis of diabetes, offering a comprehensive view of blood sugar trends over time. By understanding the test’s role and the factors that influence its results, individuals can take meaningful steps toward better health. Whether you’re newly diagnosed, managing diabetes, or at risk, regular A1c testing provides valuable insights that guide treatment plans and lifestyle choices.
It goes beyond just numbers, empowering you to make informed decisions, set realistic goals, and proactively navigate your health journey. With ongoing advancements in testing methods and resources, there are more tools than ever to help achieve optimal diabetes management. Remember, the path to better health involves not just understanding your A1c but using it as a foundation for continuous improvement and support along the way.
Citations
American Diabetes Association (ADA) – The ADA is a leading authority on diabetes management and often publishes guidelines and standards for A1c testing and blood sugar monitoring. Their website is a comprehensive resource for current information about diabetes care.
- Website: www.diabetes.org
Mayo Clinic – This respected medical institution provides patient-friendly explanations about various medical tests, including the A1c test, and offers guidance on interpreting results.
- Website: www.mayoclinic.org
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC offers resources on diabetes prevention, management, and the role of A1c in monitoring blood sugar levels.
- Website: www.cdc.gov
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) – Part of the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), the NIDDK provides detailed information on diabetes, including educational resources for managing blood sugar levels.
- Website: www.niddk.nih.gov
WebMD – Although not a peer-reviewed source, WebMD can be used for general explanations and overviews of medical tests, including the A1c test. It is a popular source for patient information.
- Website: www.webmd.com
Additional Resources
Be sure to check out our YouTube Channel! While you’re at it, we have some must reads recommended by our Dudes, such as, What Are The First Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes?.



